Introduction
Embedded Systems and IoT solutions rely heavily on sensors to interact with the physical world. A sensor is an electronic device that detects physical, chemical, or biological changes and converts them into a readable electrical signal such as:
-
Voltage
-
Current
-
Resistance
-
Digital data
These signals are processed by microcontrollers, processors, or SoCs in Embedded and IoT systems.
- Classification of Sensors Used in Embedded IoT
Sensors can be classified based on what they measure and how they interface with embedded controllers.
- Environmental Sensors
- Motion & Position Sensors
- Light & Optical Sensors
- Mechanical & Force Sensors
- Electrical Sensors
- Chemical & Biomedical Sensors
- Touch & Interface Sensors
Sensor Interface Types Most Common in Embedded Systems
- Analog (ADC)
- UART
- I2C
- SPI
- 1-Wire
- PWM
Choosing the right interface depends on:
-
Accuracy
-
Speed
-
Power consumption
-
MCU capability
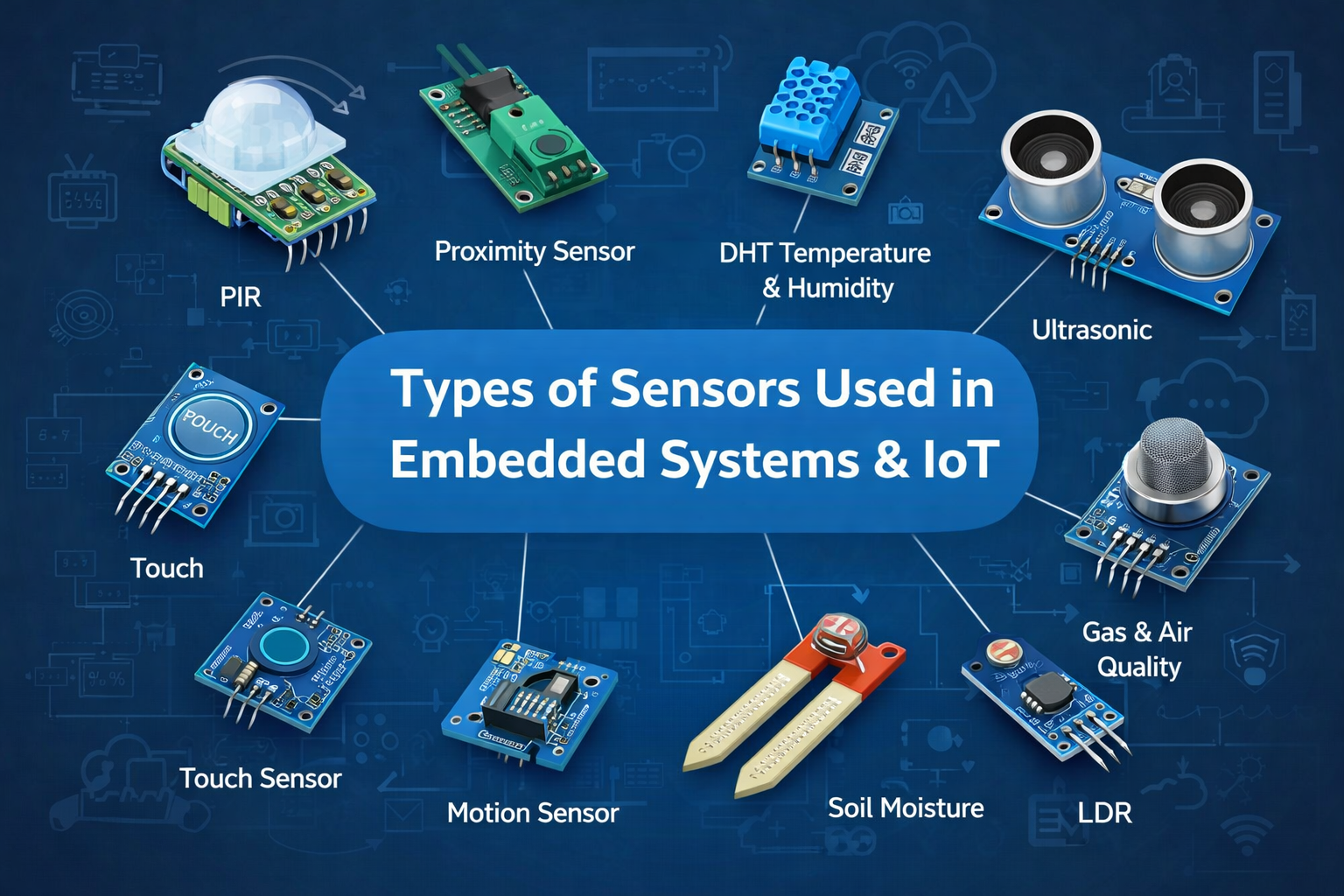
List of Commonly Used Sensors
- Temperature
- Humidity
- Pressure
- Gas
- Air Quality Sensor
- PIR Sensor or Motion
- Ultrasonic Distance Sensor
- Accelerometer
- Gyroscope
- Load Cell
- Proximity Sensor
- Force Sensitive Resistor
- Strain Gauge
- Piezoelectric Sensor
- Current Sensor
- Voltage Sensor
- Power Monitoring Sensor
- pH Sensor
- Soil Moisture Sensor
- Heart Rate Sensor
- SpO2 Sensor
- Capacitive Touch Sensor
- Resistive Touch Sensor
- Fingerprint Sensor
- Gesture Sensor
- Smoke Sensor
- Light Sensor
- RFID
- Infraded IR Sensor
Conclusion
Sensors play a critical role in Embedded Systems and IoT by enabling real-world interaction. Understanding sensor types, working principles, and applications helps engineers design reliable, scalable, and efficient systems.